Men are more at risk of heart attacks due to predisposing genetic factors and higher levels of testosterone. These factors can lead to the development of coronary artery disease, resulting in a higher likelihood of heart attacks in men.
Heart attacks are a leading cause of death globally, and understanding the reasons behind this gender disparity can help in the development of targeted prevention and treatment strategies. By addressing the specific risk factors that affect men, such as elevated testosterone levels and genetic predisposition, medical professionals and individuals can work together to reduce the incidence of heart attacks in men.
This is crucial for promoting overall heart health and reducing the burden of cardiovascular diseases on the male population.
Credit: www.cdc.gov
Understanding The Biological Factors
Men are more susceptible to heart attacks due to various biological factors that affect their cardiovascular systems. Understanding these factors is crucial to developing effective preventive measures. Genetic predisposition and hormonal influence play significant roles in increasing the risk of heart attacks in men.
Genetic Predisposition
The genetic predisposition to heart attacks is a key biological factor affecting men. Family history plays a crucial role, as individuals with a family history of heart disease are at a higher risk. Certain genetic markers and mutations can also predispose men to heart attacks. Factors such as high cholesterol levels, hypertension, and other cardiovascular diseases can be inherited, contributing to an increased risk of heart attacks. Understanding these genetic factors can aid in early identification and proactive management of the risk.
Hormonal Influence
Hormonal influence also plays a significant role in the increased risk of heart attacks in men. Testosterone, the primary male hormone, has been linked to atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries. While estrogen has been found to have protective effects on the cardiovascular system, the absence of this hormone in men can contribute to a higher risk of heart attacks. Moreover, hormonal changes during stressful situations can also affect the heart’s function and increase the risk of a sudden cardiac event.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in determining an individual’s risk of a heart attack. While both men and women are susceptible to heart-related issues, men are generally more vulnerable due to certain lifestyle choices that can increase the risk of heart attacks. Addressing these lifestyle factors is essential for promoting heart health and reducing the incidence of heart attacks among men.
Dietary Habits
The dietary habits followed by men significantly impact their risk of a heart attack. High consumption of saturated fats, cholesterol, and trans fats can lead to the accumulation of plaque in the blood vessels, increasing the chances of a heart attack. Excessive salt intake can also contribute to hypertension, a risk factor for heart disease. Diets lacking in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains deprive the body of essential nutrients and antioxidants that support cardiovascular health.
Physical Activity Levels
Men’s physical activity levels have a direct impact on their heart health. Inactive lifestyles can lead to weight gain, high blood pressure, and abnormal lipid profiles, all of which elevate the risk of heart attack. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, and improves overall cardiovascular function. Sedentary behaviors, such as prolonged sitting or minimal movement, can increase the likelihood of developing heart disease.
Occupational And Socioeconomic Factors
Occupational and socioeconomic factors play a significant role in the increased risk of heart attacks among men. Various stressors and societal conditions related to employment and socioeconomic status can significantly impact men’s heart health.
Stress And Work-related Pressure
Men often face significant stress and pressure in their workplaces, which can contribute to an increased risk of heart attacks. High-demand occupations that involve long work hours, deadlines, and intense pressure can elevate stress levels. These stressors, especially when chronic, can negatively impact cardiovascular health and contribute to a higher likelihood of experiencing a heart attack.
Impact Of Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status has a direct correlation with the risk of heart attacks. Men from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often face challenges such as limited access to quality healthcare, unhealthy living conditions, and insufficient resources for proper nutrition and physical activity. These factors can significantly increase the likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases and experiencing a heart attack.
Psychological And Emotional Influences
Psychological and emotional influences play a significant role in understanding why men are more at risk of heart attacks. From mental health stigma to coping mechanisms and support systems, the psychological and emotional well-being of men can have a profound impact on their heart health.
Mental Health Stigma
One of the contributing factors to the increased risk of heart attacks among men is the prevalent stigma surrounding mental health issues. The societal expectations for men to be stoic and resilient often lead to a reluctance to seek help for psychological distress. This stigma can lead to unaddressed stress, anxiety, and depression, which are major risk factors for heart disease.
Coping Mechanisms And Support Systems
Men often rely on different coping mechanisms to deal with stress and emotional challenges. Some may resort to unhealthy behaviors such as excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, or overeating as a way to cope. Additionally, the lack of supportive networks and effective communication channels can further exacerbate their vulnerability to heart attacks.
Variances In Symptoms And Diagnosis
The variances in symptoms and diagnosis of heart attacks between men and women are crucial to understanding why men are more at risk. Recognizing atypical symptoms and gender disparities in diagnosis play a significant role in this disparity.
Recognizing Atypical Symptoms
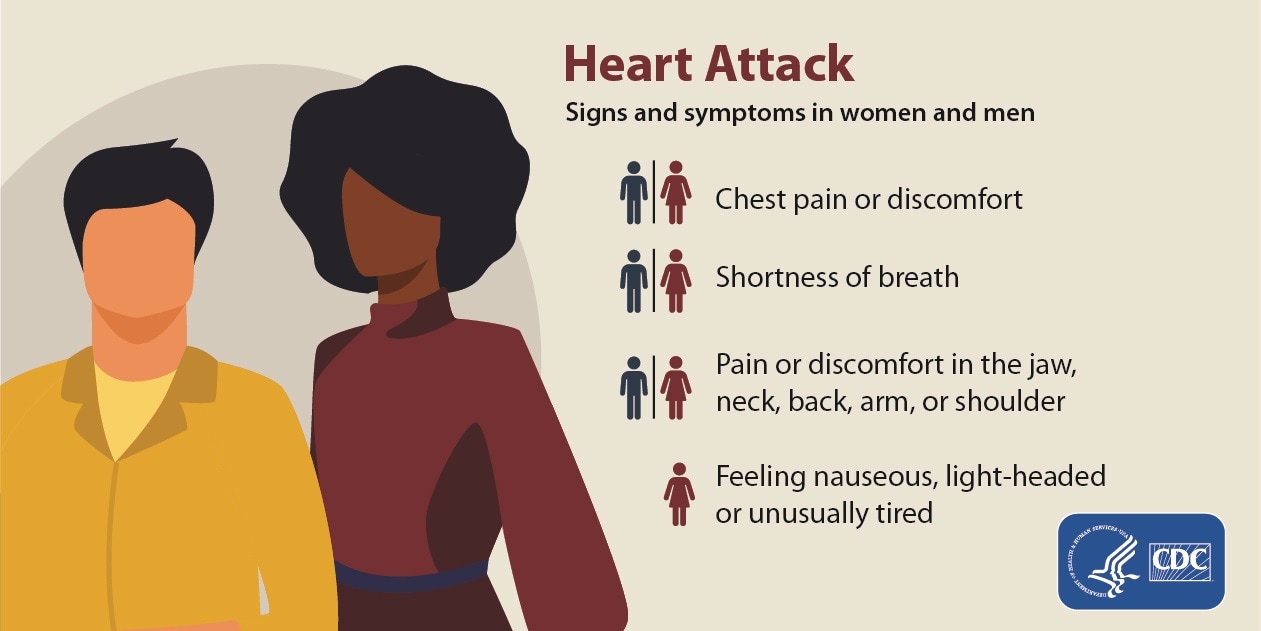
Heart attacks in men can present with classic symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and discomfort in the upper body. However, men are more likely to experience atypical symptoms that might not immediately be associated with a heart attack, such as nausea, indigestion, and jaw pain. These atypical symptoms can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, increasing the risk of severe complications.
Gender Disparities In Diagnosis
When it comes to diagnosis, studies have shown that men are more likely to receive prompt medical attention and appropriate tests when presenting with symptoms of a heart attack compared to women. This gender disparity in diagnosis can lead to underestimation of risk in men and overestimation in women, ultimately affecting the timely initiation of life-saving treatments.
Treatment Disparities
Treatment disparities can play a significant role in the increased risk of heart attacks among men. Understanding the factors contributing to these disparities is crucial to addressing the challenges faced in providing equitable care for all patients.
Access To Specialized Care
Access to specialized cardiovascular care is essential to effectively managing the risk factors associated with heart disease. However, men often encounter obstacles in accessing these specialized services, leading to delayed or inadequate treatment.
Adherence To Treatment Plans
Adherence to treatment plans is vital for reducing the risk of heart attacks, yet disparities exist in how well men are able to follow these plans. Factors such as socioeconomic status, education level, and access to resources can impact their ability to consistently adhere to prescribed treatments and medication regimens.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing heart attacks in men requires gender-tailored education and advocacy for gender-specific research. By understanding the unique risk factors and needs of men, proactive measures can be implemented to reduce the likelihood of heart attacks.
Gender-tailored Education
Educating men on the specific factors that make them more susceptible to heart attacks is crucial. Providing targeted information on lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and stress management, can empower men to make informed decisions to mitigate their risk.
Advocacy For Gender-specific Research
Advocating for gender-specific research enables the development of effective preventive strategies tailored to men’s unique needs. By supporting initiatives that focus on understanding the biological and behavioral differences in heart disease, better preventive measures can be created.
Frequently Asked Questions on Why Are Men More At Risk Of Heart Attack?
What Are the Common Signs of a Heart Attack in Men?
A heart attack in men may present as chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, and pain in the arms, back, neck, or jaw. Symptoms may also include nausea, lightheadedness, and cold sweats. It’s important to recognize these signs and seek immediate medical attention.
How Does Age Affect the Risk of Heart Attack in Men?
As men age, the risk of heart attack increases, with factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking contributing to this risk. Additionally, lifestyle choices and genetic predisposition play a role. Regular health check-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are vital for minimizing this risk.
Can stress contribute to heart attacks in men?
High levels of stress can elevate the risk of a heart attack in men. Stress triggers the release of adrenaline and cortisol, leading to an increased heart rate and blood pressure. It also promotes unhealthy habits like smoking, overeating, and alcohol consumption.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques and a healthy lifestyle is crucial.
Conclusion
Understanding the risk factors for heart attack in men is crucial for prevention. By addressing lifestyle choices, stress management, and regular health check-ups, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of heart disease. By raising awareness and making informed decisions, men can take proactive steps to safeguard their heart health for a fulfilling and healthy life.
